Institute for Biomedicine - Projects - PROTECTMOVE
PROTECTMOVE
Identifying Parkinson’s disease penetrance-modifying factors in the population-based Cooperative Health Research in South Tyrol (CHRIS) cohort
- Project duration: -
- Project status: finished
- Website: http://protect-move.de/
- Institute: Institute for Biomedicine
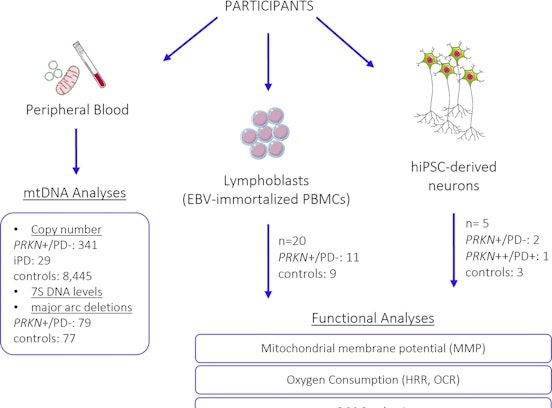
Genes causative for recessively inherited Parkinson’s disease (PD) include Parkin (PRKN) and PINK1; rare homozygous mutations in these genes result in definite symptom expression. On the other hand, evidence suggests that heterozygous mutations – a relatively common occurrence – may predispose to PD in a dominant manner with highly reduced penetrance. The largest described pedigree of PRKN mutation carriers (n=77) originates from South Tyrol and includes numerous heterozygous carriers of PRKN mutations who develop overt symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (PD), while others may have prodromal, or no obvious symptoms. In this project, we aim to dissect out the factors that modify the penetrance of these variants, using additional PRKN mutation carriers identified in the Cooperative Health Research in South Tyrol (CHRIS) study (comprising n=13,490 individuals from the same geographical region). By testing whether factors that influence mitochondrial function can alter penetrance of nuclear mutations, we observed an increased burden of heteroplasmic mtDNA mutations in affected vs. unaffected heterozygous PRKN and PINK1 mutation carriers, which might explain the phenotypic (clinical, sub-clinical) discordance in these individuals with similar nuclear genetic background. In addition, induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neurons of non-PD manifesting heterozygous mutation carriers displayed several phenotypes of altered mitochondrial function. This project was part of the DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) funded research group ProtectMove (FOR2488).
Del Greco MF, Pontali G, Foco L, Pattaro C (2024)
Presentation/Speech
Conference: 45th Annual Conference of the International Society for Clinical Biostatistics | Thessaloniki | 21.7.2024 - 25.7.2024
Gilmozzi V, Lang M, Pramstaller PP, Pichler I (2023)
Presentation/Speech
Conference: MitoPorto | Porto | 12.5.2023 - 13.5.2023
Lang M, Gilmozzi V, Pramstaller PP, Pichler I (2023)
Presentation/Speech
Conference: EUROMIT 2023 - International meeting on mitochondrial pathology | Bologna | 11.6.2023 - 15.6.2023
More information: https://euromit2023.eu/
Castelo Rueda MP, Zanon A, Gilmozzi V, Lavdas AA, Raftopoulou AA, Delcambre S, Del Greco M F, Klein C, Grünewald A, Pramstaller PP, Hicks AA, Pichler I (2023)
Journal article
npj Parkinson's Disease
Pontali G, Filosi M, Borsche M, König I, Paglia G, Foco L, Del Greco MF (2023)
Presentation/Speech
Conference: 44th Annual Conference of the International Society for Clinical Biostatistics (ISCB2023) | Milan | 27.8.2023 - 31.8.2023
Castelo Rueda MP, Gilmozzi V, Riekschnitz DA, Di Segni M, Silipigni R, Pramstaller PP, Hicks AA, Pichler I, Zanon A (2022)
Journal article
Stem Cell Research
Bottigliengo D, Foco L, Seibler P, Klein C, König IR, Del Greco M F
(2022)
Journal article
Brain
Kappen S, Bottigliengo D, Caliebe A, Del Greco M F, König IR (2022)
Journal article
Medizinische Genetik
More information: https://doi.org/10.1515/medgen-2022-2139
Trinh J, Hicks AA, König IR, Delcambre S, Lüth T, Schaake S, Wasner K, Ghelfi J, Borsche M, Vilariño-Güell C, Hentati F, Germer EL, Bauer P, Takanashi M, Kostić V, Lang AE, Brüggemann N, Pramstaller PP, Pichler I, Rajput A, Hattori N, Farrer MJ, Lohmann K, Weissensteiner H, May P, Klein C, Grünewald A
(2022)
Journal article
Brain
Castelo-Rueda MP, Zanon A, Gilmozzi V, Lavdas AA, Raftopoulou A, Delcambre S, Del Greco M F, Klein C, Grünewald A, Pramstaller PP, Hicks AA, Pichler I (2022)
Presentation/Speech
Conference: Cell Symposia| Multifaceted Mitochondria | Seville : 6.11.2022 - 8.11.2022
Bottigliengo D, Foco L, Seibler P, Klein C, König IR, Del Greco MF (2021)
Conference proceedings article
Conference: XI Congresso Nazionale SISMEC | Bari | 15.9.2021 - 18.9.2021
Bottigliengo D, Foco L, Seibler P, Klein C, König IR, Del Greco M F (2021)
Conference proceedings article
Conference: 2021 IGES Annual Meeting | | 13.10.2021 - 16.9.2021
More information: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/gepi.22431
Bottigliengo D, Caliebe A, König IR, Del Greco M F (2021)
Conference proceedings article
Conference: 42nd Annual Conference of the International Society for Clinical Biostatistics (ISCB42) Conference | Lyon | 18.7.2021 - 22.9.2021
More information: http://www.iscb2021.info/en
Castelo-Rueda MP, Zanon A, Gilmozzi V, Klein C, Pramstaller PP, Hicks AA, Pichler I (2021)
Presentation/Speech
Conference: 22nd International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders | virtual | 17.9.2021 - 21.9.2021
Castelo Rueda MP, Raftopoulou A, Gögele M, Borsche M, Emmert D, Fuchsberger C, Hantikainen EM, Vukovic V, Klein C, Pramstaller PP, Pichler I, Hicks AA (2021)
Journal article
Frontiers in Neurology
More information: https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.706145
Prasuhn J, Borsche M, Hicks AA, Goegele M, Egger C, Kritzinger C Pichler I, Castelo-Rueda MP, Langlott L, Kasten M, Mascalzoni D, Klein C, Pramstaller PP, Brueggemann N (2021)
Journal article
Parkinsonism & Related Disorders
Castelo MP, Trinh J, Zanon A, Rainer J, Bauer P, Kandaswamy KK, Werber M, Rolfs A, Grunewald A, Borsche M, Lohmann K, Klein C, Pramstaller PP, Pichler I, Hicks A (2019)
Presentation/Speech
Conference: International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders | Nice | 22.9.2019 - 26.9.2019