magazine_ Article
To K2!
A project by Eurac Research is investigating the physiology of eight female mountaineers on their way to climb the second highest mountain on Earth
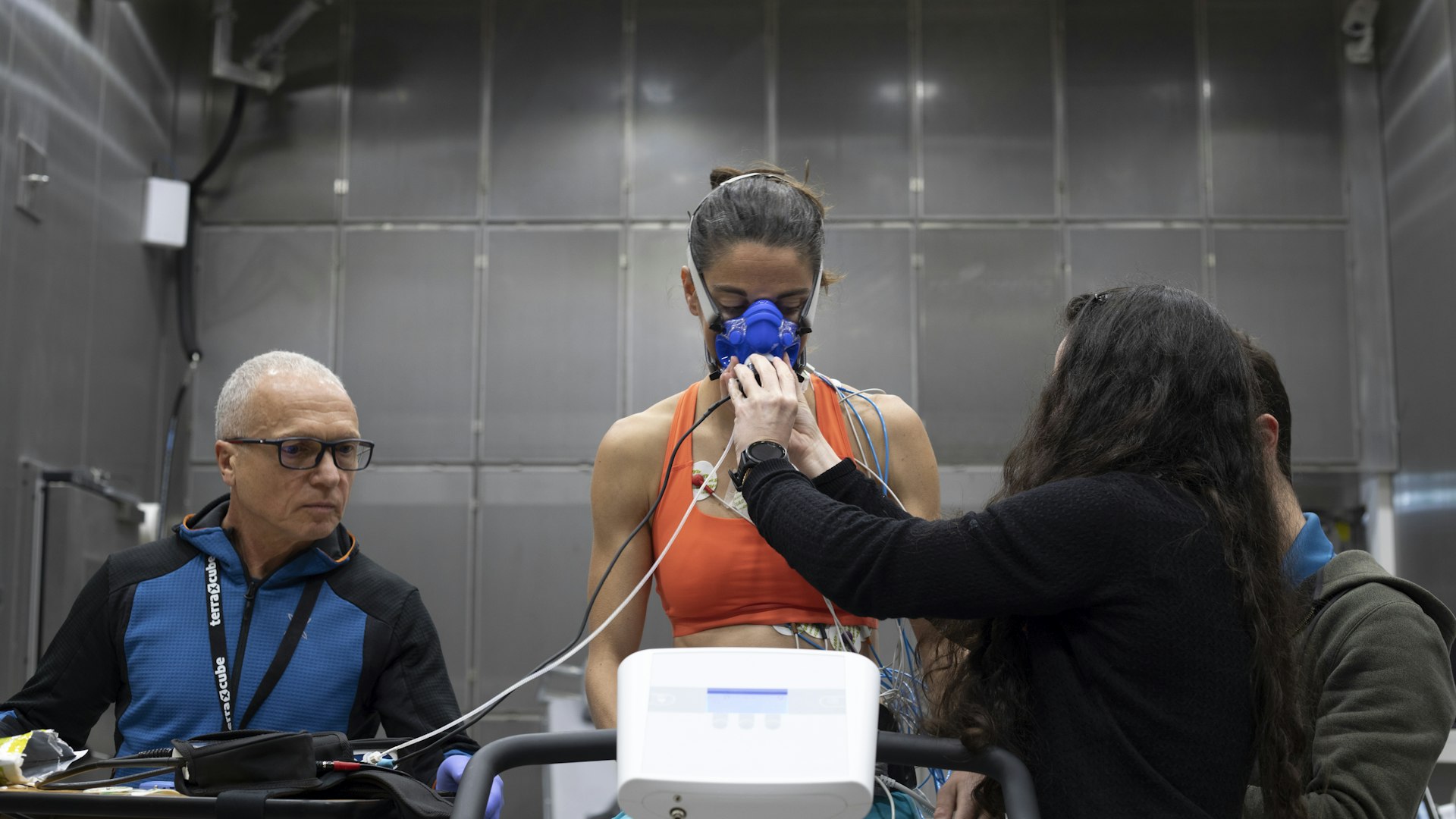
Mountaineer Silvia Loreggian undergoes one of the medical tests aimed at examining her physiological response to high altitude.
Seventy years after its first summiting, an equally divided cohort of eight female mountaineers from Italy and Pakistan, will attempt to climb the world's second highest peak: K2. The initiative, sponsored by the Italian Alpine Club, involves Eurac Research’s Institute for Mountain Emergency Medicine. The mountaineers underwent a series of preliminary tests at our extreme environment simulator – terraXcube. Once their adventure is over, they will return to undergo more tests in the unique infrastructure. The research mission: study female physiology before and after exposure to high altitude.
With the exception of some populations, humans are not adapted to live above a certain altitude. The reduction in air pressure that takes place as altitude increases makes it increasingly difficult to oxygenate the blood and, consequently, other body tissues.
High altitude and hypoxia
The air above us exerts a certain level of atmospheric pressure on every surface it contacts. As we rise in altitude, the amount of air bearing down on us decreases, and with it, atmospheric pressure also decreases, as does the pressure exerted by each of the gases in the air itself. Among these gases is oxygen. At the summit of Mont Blanc – 4,807 m.a.s.l, the partial pressure of oxygen is little more than half that found at sea level. Above 8,000 m.a.s.l, one enters the so-called “death zone” where the partial pressure of oxygen is so low that it would be impossible to survive for more than a few hours. The lower the oxygen pressure in the air, in fact, the more difficult it will be to pass into the blood from the lungs. Poor oxygenation of the blood results in poor oxygenation of other tissues, a condition known as hypoxia.
Oxygen deficiency triggers several physiological responses, including increased heart and respiratory rates, dilation of cerebral and muscular blood vessels, and constriction of pulmonary blood vessels. While these physiological changes temporarily make up for the lack of oxygen in the tissues, they also underlie the symptoms of acute mountain sickness. Being at high altitude without having acclimatized first, that is, without having given the body time to adapt to hypoxia, can result in headaches, nausea, insomnia, sleep apnea, even, in severe cases, hallucinations, and pulmonary and cerebral edema.
Much of what is known about the effects of high altitude on the human body comes from studies conducted on male subjects.
Much of what is known about the effects of high altitude on the human body comes from studies conducted on male subjects. The paucity of data on female physiology at high altitudes is not only surprising, considering that women have been climbing mountains since the advent of modern mountaineering, but also dangerous: having such little data means that ad hoc medical recommendations for female mountaineers are likely to be unreliable. In light of this, the women’s ascent of K2, organized by the Italian Alpine Club on the 70th anniversary of the summit’s conquest, presents a golden opportunity.
The women’s ascent of K2 presents a golden opportunity.


Before their expedition, the eight Italian and Pakistani mountaineers stopped by terraXcube where, under the guidance of researchers from Eurac Research’s Institute for Mountain Emergency Medicine, CeRiSM – the Sport, Mountain and Health Research Center in Rovereto –, Italian Alpine Club and Institute of Clinical Physiology, the group underwent a series of tests. These were carried out both at Bolzano’s altitude and at the simulated altitude of 5,000 m.a.s.l: the same altitude at which the K2 base camp is located. Among the examinations performed, various blood samples, tests and analyses designed to assess cardiovascular and respiratory function both at rest and during exercise, such as ultrasound scans and spirometry, and brain function, as well as computer-based cognitive tests were carried out on the female subjects. The latter took into account reaction speed, short-term memory, and the ability to process visual-spatial information.










In June, the mountaineers will fly to Pakistan and, once acclimatization is achieved, attempt the summit in the second half of July. Having concluded their adventure, they will return to the terraXcube to repeat the tests carried out before their departure, and more. When they return, in fact, their acclimatization level will be such that they can be safely exposed to simulated altitudes above 8,000 m.a.s.l. Comparing the results of the experiments carried out before their departure with those obtained on this second occasion will shed light on how the female organism functions at extreme altitudes. An important contribution to the resolution of gender disparities in the biomedical field.
Federica Mingolla, Silvia Loreggian, Anna Torretta and Cristina Piolini, the four Italian mountaineers taking part in the expedition, introduce us to the world of extreme mountaineering.
Expedition doctor Lorenza Pratali and the director of the Institute for Mountain Emergency Medicine Giacomo Strapazzon talk to us about the physiology of the human body at extreme altitudes.